HERNIATED DISC
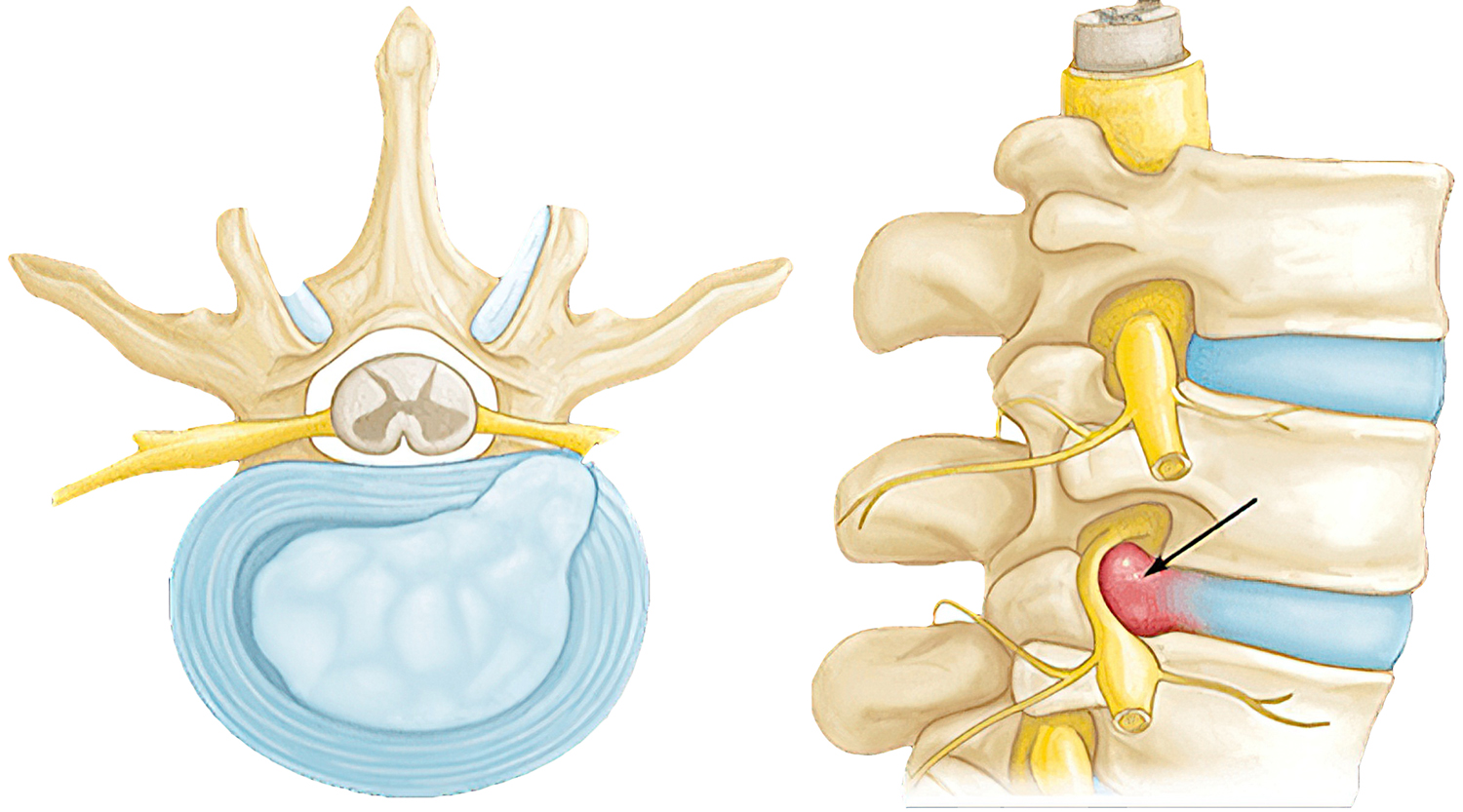
What is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc occurs when a portion of the vertebral disc ruptures. Through the ruptured portion, the inner central portion of the disc (nucleus pulposus) is pushed out into the spinal canal on nerves in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar areas.
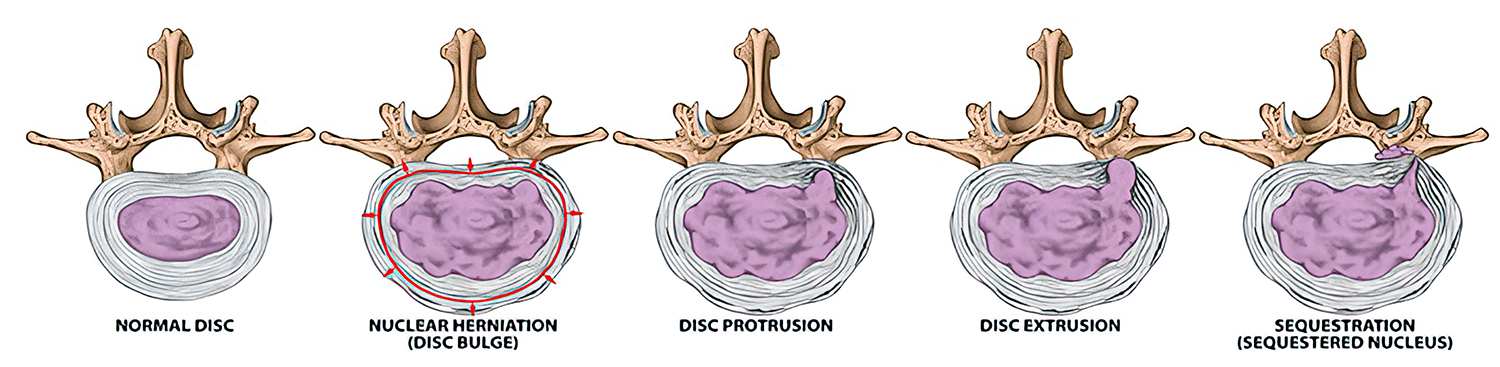
Because the spinal canal has limited space, the displaced disc presses on the nerves which can often lead to numbness and pain. Smaller herniations are sometimes called protrusions.
Continue reading about the causes and symptoms of a herniated disc, or use the following link to learn about the possible treatment options for herniated discs.
Symptoms
Cervical Herniated Disc Symptoms
- Discomfort in one or both arms
- Shooting pains in one or both arms
- Weakness or numbness in one or both arms
- Burning arm pain
Lumbar Herniated Disc Symptoms
- Discomfort in the leg, ankle, or foot
- Shooting pain, weakness, or numbness in the leg
- Leg pain is usually worse when sitting
Causes
Cervical Herniated Disc Causes
- Degeneration due to the normal aging process
- Trauma
- An episode of lifting a heavy object
Lumbar Herniated Disc Causes
- Degeneration due to the normal aging process
- Trauma
- An episode of lifting a heavy object
- Sudden twisting
Herniated Disc Treatments

Herniated Disc Diagnosis
To properly diagnose a herniated disc, your orthopedic doctor may order imaging tests such as X-Rays, MRIs, or CT scans. A CT Scan and/or MRI can show the soft tissue of herniated discs. Furthermore, it can also show the actual stage and location of the herniation. At TriMed Spine & Joint, our orthopedic doctors and surgeons specialize in treating herniated discs. Our facilities are also equipped for proper and efficient diagnosis of a herniated disc such as digital X-Rays, MRI equipment, a Laboratory, and a Procedure Suite.
Herniated Disc Symptoms & Treatment Options
A herniated disc (also known as a bulging disc, ruptured disc, or slipped disc) occurs when a portion of the vertebral disc ruptures. Through the ruptured portion, the inner central portion of the disc (nucleus pulposus) is pushed out into the spinal canal on nerves in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar areas. Because the spinal canal has limited space, the displaced disc presses on the nerves which can often lead to numbness and pain. A smaller herniation is sometimes called protrusion.
The most common causes of disc herniation include:
- Degeneration due to the normal aging process
- Trauma or injury
- An episode of heavy lifting
- Sudden twisting
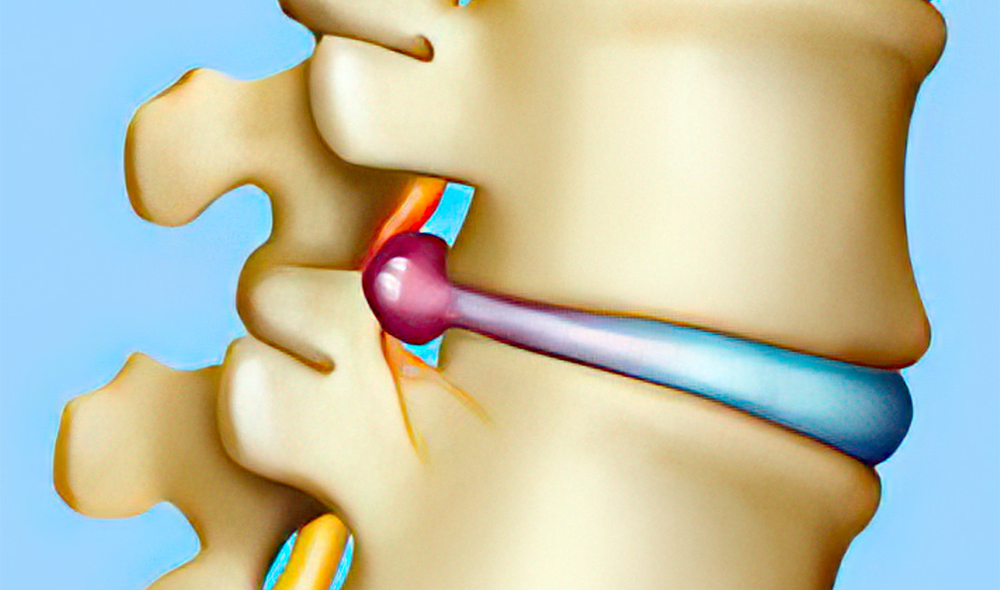
Common Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
- If the herniation occurs in the upper back (cervical spine), you may experience discomfort, shooting pains, burning pain, and weakness or numbness in one or both arms
- If the herniation occurs in the lower back (lumbar spine), you may experience discomfort in the leg, ankle, or foot; shooting pain, weakness, or numbness in the leg. Furthermore, leg pain is usually worse when sitting.
- Muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling are very common when there is disc herniation.
Herniated Disc Diagnosis
Most people tend to think that they simply walk off a physical problem, but there is a moment when the pain and the interruption of your daily activities bring you to the doctor since you want to understand why and what to do. Well, for a proper disc herniation diagnosis, your orthopedic doctor will ask you questions and perform some tests in order to locate the source of your pain and pinpoint the herniated disc.
Your doctor will execute a neurological exam in order to test sensitivity, reflexes, muscle strength, nerve reactions, and pain spread. This is very useful for both the doctor and the patient to understand the type of pain or source of it. For example, a patient may experience leg pain; but after some tests, he’ll understand that this is Radicular Pain that can originate in the lower spine where the herniated disc is pressing on the sciatic nerve that travels down the leg.
To confirm (and visualize) a herniated disc, some imaging tests may be ordered by your doctors such as X-Rays, MRIs, or CT scans. X-Rays are used to pretty much rule out physical abnormalities of the spine. Typically, x-rays are not used alone to diagnose herniated discs. A CT Scan and an MRI can show soft tissue of herniated discs showing the actual stage and location of the herniation for proper treatment.
At Spine & Orthopedic Center, our facilities have experienced orthopedic doctors and surgeons with several years of experience treating herniated discs, but state-of-the-art in-house equipment as well for proper and efficient diagnosis such as digital X-Rays, MRI equipment, Laboratory, and Procedure suites.
Disc Herniation Treatments
The possible treatment for a herniated disc is evaluated and discussed only after a careful examination, tests, and proper diagnosis. There are always non-surgical and surgical options to treat a herniated disc which depend on the degree of the herniation and the patient’s response to the non-invasive treatments.
Non Operative Treatments
Medications and non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy are sometimes needed. Occasionally epidural injections are indicated for pain relief (and sometimes diagnosis). Surgery can be considered for those who do not improve with a more conservative approach.
One of the basics approach of physical therapy when treating a herniated disc is targeted stretching and constant exercises for rehabilitation and to strengthen the back muscles. Epidural injections are often considered to provide pain relief so the patient can continue with the rehabilitation process.
Surgical Treatments
Nowadays, most surgical procedures to treat herniated discs are minimally invasive and do not require a hospital stay. As a matter of fact, SOC is well known for its success rate in treating a herniated disc. The following are the most common surgical procedures for disc herniation:
Anterior Cervical Discectomy Fusion Instrumented
The ruptured disc is removed. It is then replaced by a bone graft. An anterior cervical plate is implanted for stability.
Posterior Cervical Laminotomy
The spinous process and lamina are removed to decrease pressure on the spinal cord. Instrumentation may be used to increase postoperative stability.
Lumbar Partial Discectomy
Removal of the herniated portion of the disc relieves the pressure on the painful nerve.
For more information on herniated discs and possible treatment options, call our specialists today.
